Registration
Principles of DF measurement
A classical apparatus for registration of DF is the phosphoroscope (Fig. 12). It is a rotating disc with perforations (holes) placed between the light source and the measured sample. The sample is illuminated only when light passes through a hole. The rotation provides alternating light and dark periods, i.e. periodical illumination of the sample. The duration of the dark and the light periods is determined by the size of the holes, the distance between them, and the rotating speed.
The light coming from the sample during the dark periods is delayed fluorescence. Recording the emission only within the dark periods guarantees that the delayed fluorescence will be separated from both the actinic light and the fluorescence.
The FL-2006 apparatus
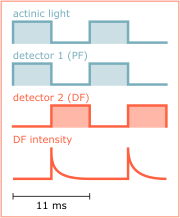
Our experiments were done using a computer-driven instrument that utilizes the basic principle of the mechanical phosporoscope but in addition to DF is capable to simultaneously register the prompt fluorescence and the DF dark decay kinetics. This is achieved by using two light detectors (photomultiplier tubes) synchronised electro-optically with the disc rotation. The first photomultiplier is switched on during the light periods of the phosphoroscope cycle and detects prompt fluorescence (Fig. 13). The other photomultiplier is switched on during the dark periods and detects delayed fluorescence. One phosphoroscope cycle lasts approximately 11 ms, with about 5.5 ms of illumination (PF detection) and 5.5 ms of darkness (DF detection). The DF intensity is digitized at 40 µs resolution which means that 130 data points of the dark decay are stored for each 5.5 ms dark period.
Taking the average intensity of PF and DF registered by FL-2006 during each consecutive cycle, we get the PF and DF induction curves. Moreover, for each point of the DF induction curve, a 5-ms dark decay curve is available. These features make FL-2006 a unique tool for studying the DFIC because each point of the DFIC can be compared to the FIC and also decomposed into individual DF kinetic compents.
Protocol for measurements
Induction curves of PF and DF are measured simultaneously from the same leaf sample using the FL-2006 fluorometer by the following protocol:
Prior to measurement plants are dark-adapted for at least 1 h. A detached leaf is clipped in the measuring chamber and the door is closed. After 1 min in darkness, the measurement starts. The intensity of the actinic light on the leaf surface is about 1200 µmol m−2 s−1. The leaf temperature during the measurement is 23 °C. ICs are registered for a period of 1 min. The data are fed to a computer for subsequent processing and analysis.