- It is established that malate dehydrogenase and esterase isozymes may be used as markers for the identification of apomictic plants in the hybrid progeny of maize with its wild relative Tripsacum dactiloides. Apomictic forms are valued genetic material for breeding programs, directed for the fixture of the heterotic effect in maize.
- The biodiversity of fungal species associated with leaf spotting of wheat was investigated in Bulgaria and Slovakia in the framework of bilateral research project between Institute of Plant Physiology and Genetics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria and Plant Production Research Center Piestany, Slovakia. Current data were obtained for the economically important and emerging pathogens on T. aestivum, T. durum and some graminicolous grasses. A pathogen collection was created.
- Tomato lines originating from three-genome hybrid (L. esculentum – L. chilense – L. peruvianum var. humifusum) with complex resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, (races R0 и R1), Xanthomonas vesicatoria (races T1, T2, T3 and pathotype РТ) and Xanthomonas perforans were developed.
- The changes in population diversity of tobamoviruses in tomato and pepper, connected with introduction of resistant to these viruses cultivars in agriculture were studied. The strains of tomato mosaic virus (ToMV), overcoming the tobamovirus resistant gene Tm-1 was isolated from commercial tomato cultivars. Pepper mild mottle virus (pathotype P1) and pepper mild mottle virus (pathotype P2) were identified from the introduced pepper cultivars grown in Bulgarian fields. The truly destructive epidemics of “veinal necrosis” disease have been observed periodically in field tomato. The necrotic stains of cucumber mosaic virus possessing fifth satellite RNA were identified as the causal agent of this disease.
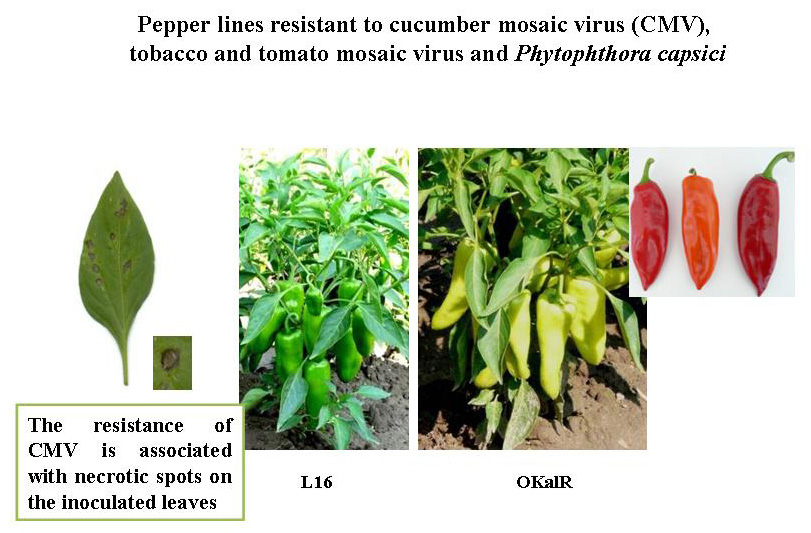
- The pyramiding of resistant genes to the most important diseases (phytophthora root rot, cucumber and tobacco mosaic diseases) and genes for good savor qualities, high quantity of b-carotene (provitamine A), vitamin C, reducing sugars, licopene, dry matter content, anthocyaninlessness in pepper lines was carried out. The developed pepper lines are suitable for early and middle early field production of sweet pepper and may be used by the plant breeders in pepper improvement programs.
- Pepper collection created during the implementation of ERA 226 project included 235 local forms, situated in Albania (17), Bulgaria (134), Greece (34), Macedonia (11) and Serbia (39). Morphological and phenological observations as well as biometric measurements on the basis of 67 features were conducted according to Descriptors for Capsicum with some additions. Significant diversity of local pepper forms was established in the collected material. Fruit shape was used as a major trait for its arrangement.
- The anthracnose disease on pepper was investigated in detail. Phenotypic, genotypic and pathogenic characterization of Colletotrichum isolates showed that the population of the causal agents of anthracnose is heterogenous and at least three species: C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides and C. coccodes were associated with the development of the disease in Bulgaria. Among them C. coccodes was the most frequently found. On the basis of comparative morphological, cultural and molecular characteristics of C. coccodes obtained from fruits and roots it was proved that the fruit anthracnose and root rot were caused by one and the same species. One unusual Colletotrichum sp. was found belonging to the C. gloeosporioides group.
- An important number of tomato (Trapezica, Bononia, Berika, Rayana F1, Rozalina-Rossa F1, Naslada F1) and maize (Zaharina F1) varieties possessing high nutritive and market quality and productivity were developed. The majority of these varieties are grown on large area in Bulgaria.

